- Risk Queue
- Posts
- Banks Get Ready For Additional Capital for Operational Risk / Complying to EU AI Standards!
Banks Get Ready For Additional Capital for Operational Risk / Complying to EU AI Standards!
ALSO: The Regulators "Unicorn Rule" & CEO's Face Pressure On Risk Management Capabilities
Welcome to our new subscribers! Thrilled to have you here. Let's dive into the Risk Queue!
-Naeem, CEO & Founder, Risk On Q
PICKS
Capital Cushion- Regulators and Large Banks are at odds.
AI Compliance, U.S. Multinational Firms will need compliance strategy to meet EU AI Standards.
Risk Management Top Priority: Citi Bank faces regulatory pressures!
Risk Headlines
US Regulators Are Planning ~20% Increase in Capital for Large Banks - source wallstreetjournal.com
Key Points:
An average ~20% increase in capital that large banks must hold as a buffer against losses. Expanding rules meant for mega-banks to those over $100 billion in assets. More banks will face heightened standards. Expect knock-on effects similar to what largest institutions have faced the past decade in terms of rigor and compliance costs.
While strengthening the overall resilience of the banking system is a worthwhile aim, there is a need to carefully evaluate the potential unintended consequences of substantially higher capital requirements. There will be a critical response period by Bank’s to conduct and provide impact analyses on the bank’s strategic direction, customers, and market activities before final rules are set. Banks focused on fee income like wealth management and investment banking may require larger capital buffers. The new rules are expected to treat fee-based activities as an operational risk, regulators are expecting this risk discipline to mature at Bank’s or expect larger fines.
Do you need assistance in managing the risk landscape?
We are ready to partner with Banks to provide a real time risk ecosystem they can have confidence in to present to shareholders, customers, and regulators. Our risk software enables Banks to demonstrate, manage, and optimize resilience enterprise-wide. Granular and early warning signals of adverse gaps allow preemptive mitigation. Regulators will demand that risk systems do more than simply check a compliance box. Our technology offers the discerning precision to truly align capital levels with underlying risks.
A.I. Risk / Technology Risk
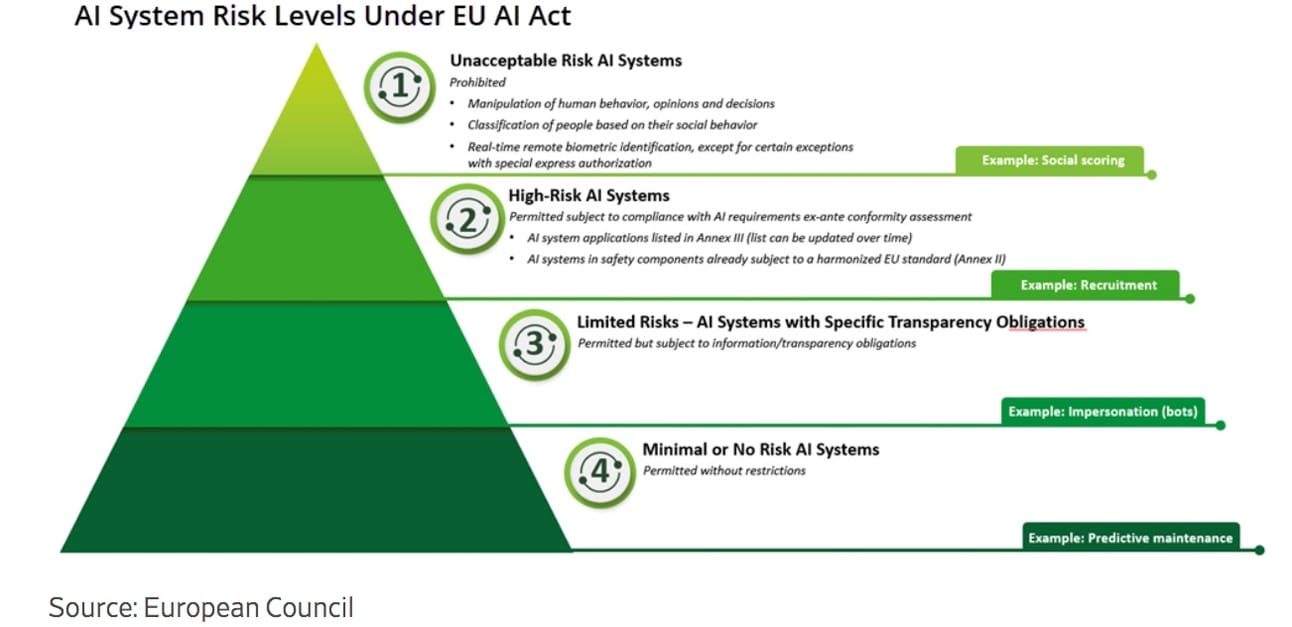
How EU AI Act May Accelerate Compliance Regime for U.S. Enterprises - source deloitte.wsj.com
Key Points:
The EU AI Act, expected to be finalized in early 2024, will apply to U.S.-based organizations deploying AI-based products or services accessible to EU citizens. It has global reach, similar to the GDPR, imposing specific requirements on providers, deployers, or distributors of AI reaching the EU market.
U.S.-based entities can prepare for compliance by taking stock of existing AI ethics and governance processes, developing coordinated strategies, assigning cross-functional responsibilities, and adopting appropriate frameworks. Compliance deadlines range from 6 to 36 months depending on the type of AI system.
Regulatory News - Fines, Losses, & Rules
SEC has charged several broker-dealers firms for failure to maintain and preserve electronic communications. The firms were charged with violating recordkeeping provisions and failing to supervise to prevent and detect violations. Each firm was ordered to cease future violations, pay penalties, and undergo compliance reviews and supervision enhancements. We have termed this regulation as the “Unicorn Rule”, as this rule alone has collected over a billion dollars for regulators.
____________________________________________________________
Citi Pressured by Regulator’s To Fix Longstanding and Widespread Risk Management Deficiencies - source reuters.gov
Citi is confronting urgent demands from regulators to fix risk, governance and oversight issues while the CEO is also spearheading a comprehensive business transformation. Speaking from experience in managing large regulatory matters Citi has a tough road ahead and there is no easy fix here, timelines are rigid and the leaders will need to set a clear vision on the strategy and execution path to meet regulatory expectations.
Emerging Risk
The 2024 Priorities for the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB)- source pcaobus.com
Key Points:
Insights into the PCAOB's staff priorities for 2024 inspections and interactions with audit committees, emphasizing areas such as inspection considerations, broker-dealers, recurring deficiencies, and critical audit matters.
Inspection Considerations: Focuses on risks and considerations important for auditors when planning and performing audits.
Broker-Dealers: Includes procedures over broker-dealers, focusing on challenges and recurring deficiencies.
Effective Practice : TestingDiscusses the selection and testing of management review controls in audits of internal control.
Recurring Deficiencies: Discusses deficiencies in audit work related to various accounts and transactions.
Evaluating Audit Evidence: Emphasizes the consideration of due professional care and the exercise of professional skepticism.
Understanding the Company: Stresses the importance of obtaining an understanding of the public company and its environment.
Use of Other Auditors: Highlights the principal auditor's responsibility to properly plan and oversee the work of other auditors.
Going Concern: Discusses the requirement for auditors to evaluate a company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Critical Audit Matters: Focuses on audit firms’ compliance with the requirements for critical audit matters.
Risk Data to Geek Out On
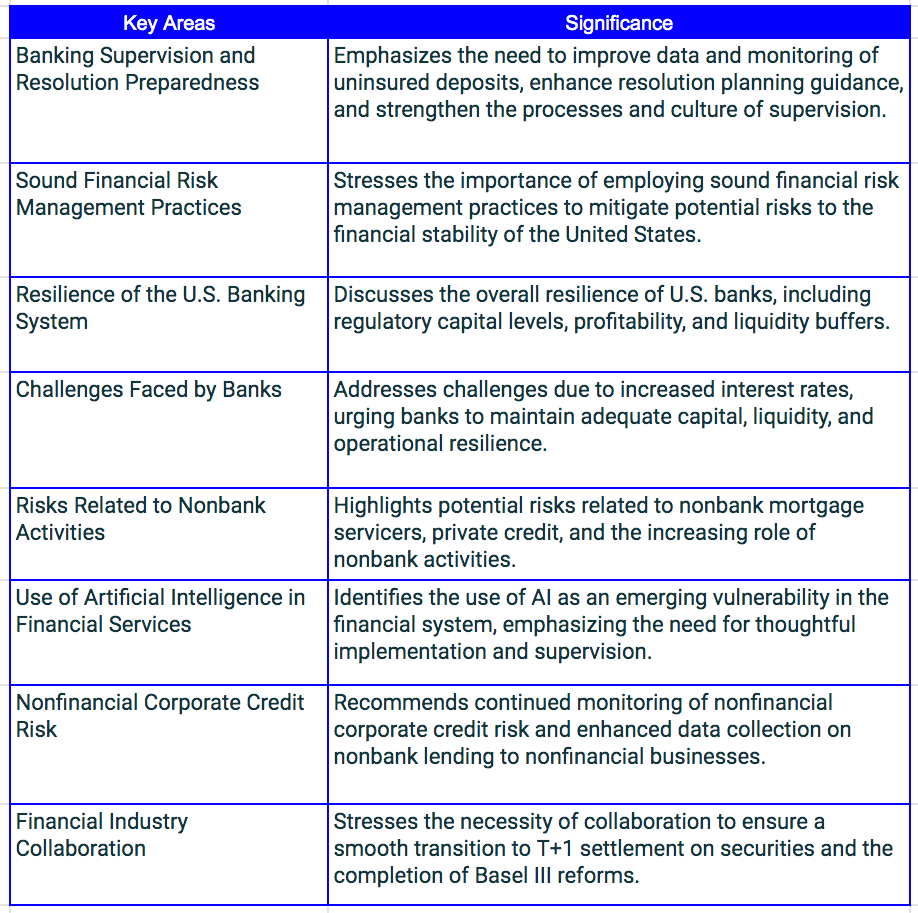
Financial Stability Oversight Council Annual Report - source treasury.gov
The Financial Stability Oversight Council (Council) was established by the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (Dodd-Frank Act) and is charged with three primary purposes:
1. To identify risks to the financial stability of the United States (U.S.) that could arise from the material financial distress or failure, or ongoing activities, of large, interconnected bank holding companies or nonbank financial companies, or that could arise outside the financial services marketplace.
2. To promote market discipline by eliminating expectations on the part of shareholders, creditors, and counterparties of such companies that the U.S. government will shield them from losses in the event of failure.
3. To respond to emerging threats to the stability of the U.S. financial system.
The Financial Stability Oversight Council's 2023 Annual Report highlights the critical areas that Banks should prioritize, including banking supervision, risk management practices, and challenges faced by banks. It emphasizes the need for enhanced data monitoring, resolution planning guidance, and sound financial risk management practices to mitigate potential risks. The report also addresses the resilience of the U.S. banking system, risks related to nonbank activities, the use of artificial intelligence in financial services, and the importance of financial industry collaboration. These areas are crucial for Banks to ensure they are well-prepared to navigate potential risks and maintain financial stability.
_________________________________
Thank you for reading,
Naeem
p.s. If you find the Risk Queue newsletter helpful please subscribe and share it with a friend or colleagues, you can find it here


